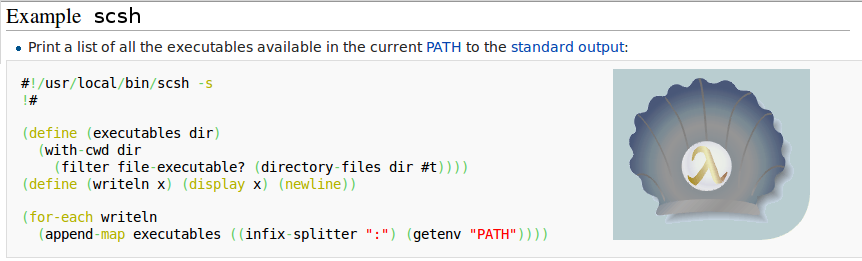
scsh
At the scripting level, scsh also has an Awk design, also implemented as a macro that can be embedded inside general Scheme code.
Scsh additionally provides the low-level access to the operating system normally associated with C. The current release provides full access to POSIX, plus important non-POSIX extensions, such as complete sockets support. "Complete POSIX" means: fork, exec & wait, sockets, full read, write, open & close, seek & tell, complete file-system access, including stat, chmod/chgrp/chown, symlink, FIFO & directory access, tty & pty support, file locking, pipes, select, file-name pattern-matching, time & date, environment variables, signal handlers, and more.
Please be aware that several of the other scheme implementations being distributed as Debian packages also provide much of the similar system programming functionality. It is wisest to try them all and explore.
This package is a dependency package, which depends on Debian's default scsh version (currently v0.6).